Tata Comm

Analysing Starlink's upstreams in India
Cloudflare DNS outage & BGP route hijack
High latency between India and Europe
Analysing transit free networks
Inefficient IGP can make eBGP go wild!
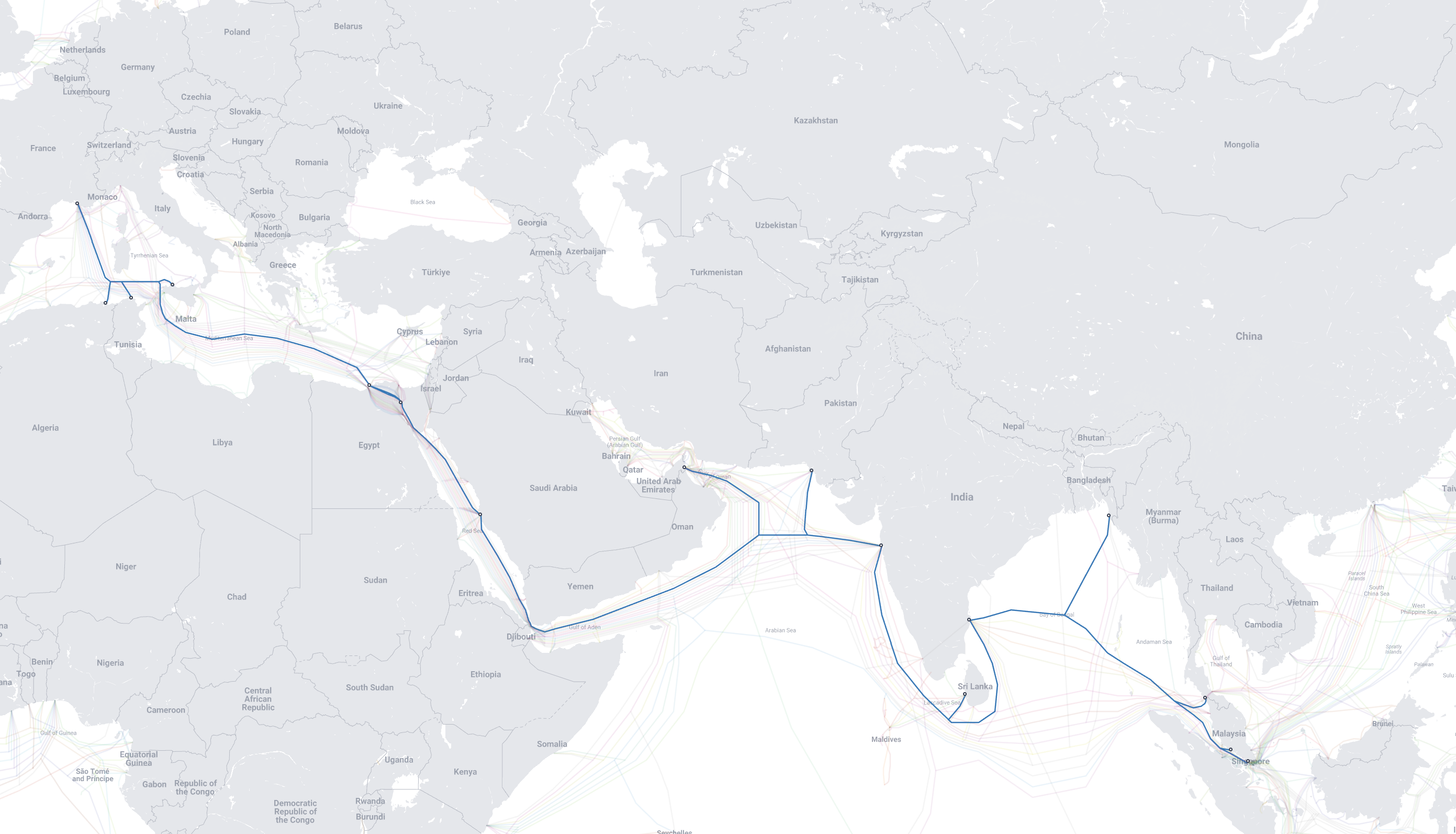
Lately, I have been struggling to keep latency in check between my servers in India and Europe. Since Nov 2021 multiple submarine cables are down impacting significant capacity between Europe & India. The impact was largely on Airtel earlier but also happened on Tata Comm for a short duration. As of now Airtel is still routing traffic from Europe > India towards downstream networks via the Pacific route via EU > US East > US West > Singapore path. Anyways, this blog post is not about the submarine cable issue.
Why Indian internet traffic routes from outside of India?
After my last post about home networking, I am jumping back into global routing. More specifically how Indian traffic is hitting the globe when it does not need to. This is an old discussion across senior management folks in telcos, policymakers, and more. It’s about “Does Indian internet traffic routes from outside of India?” and if the answer is yes then “Why?” and “How much?”
It became a hot topic, especially after the Snowden leaks. There was even an advisory back in 2018 from Deputy National Security Advisor to ensure Indian internet traffic stays local (news here). Over time this has come up a few dozen times in my discussion with senior members from the Indian ISP community, individuals, and even latency-sensitive gamers. So I am going to document some of that part here. I am going to put whatever can be verified publically and going to avoid putting any private discussions I had with friends in these respective networks. The data specially traceroutes will have measurement IDs from RIPE Atlas so they can be independently verified by other network engineers.