DNS hack of Google, Facebook more sites in .bd
Yesterday Google’s Bangladeshi website google.com.bd was hacked and this happened via DNS. It was reported on the bdNOG mailing list at morning in a thread started by Mr Omar Ali.
This clearly shows how authoritative DNS for “com.bd.” (which is same as bd. btw) was poisoned and was reflecting attackers authoritative DNS. Later Mr Farhad Ahmed posted a screenshot of google.com.bd showing hackers page:
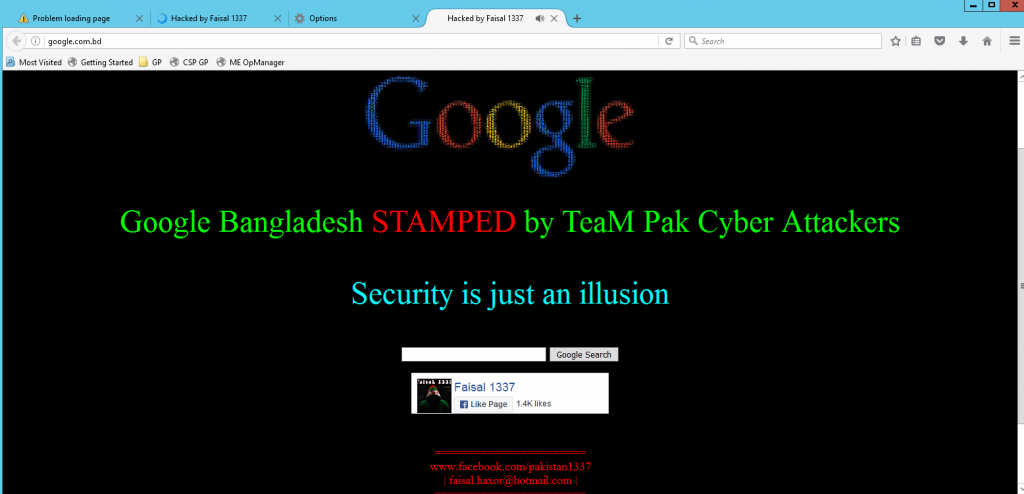
Later Mr Sumon Ahmed mentioned that it happened because web frontend of .bd was compromised. This was an interesting hijack as attacker attacked the key infrastructure of the registry instead of Google or Facebook servers. It’s also a warm reminder of the way DNS depends on the hierarchal structure by design and at this stage, we need to focus on DNSSEC to add on the security to the current system. Lately .bd domain faced issues multiple time this year. I hope it will have a good stable time in the upcoming year. In terms of stability it is being backed by PCH anycast infrastructure but PCH’s DNS servers are just published in NS records of it’s existing auth servers, but not on the parent zone (which is root zone). Thus the point of failure remains and is yet to be fixed.